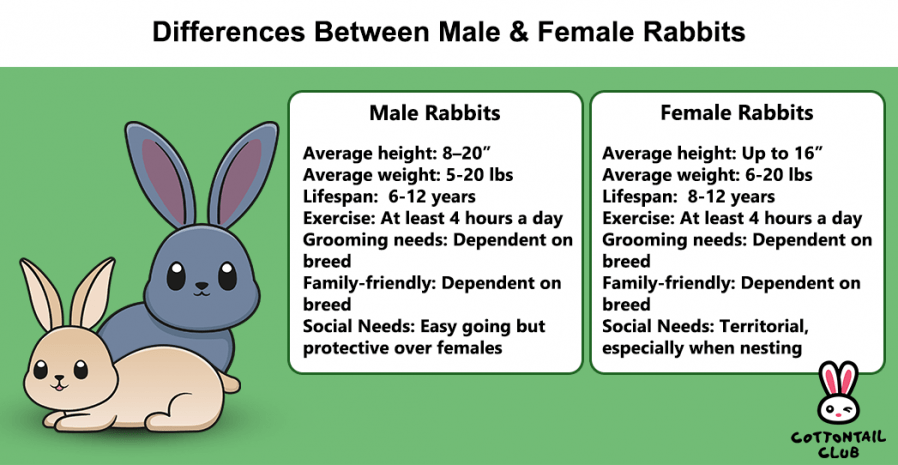
Knowing the differences between male and female rabbits can be important for both pet owners and individuals trying to identify wild rabbits. Despite not having significant differences in size or appearance, there are certain distinguishing characteristics between the two genders. For instance, some female domestic rabbits have dewlaps, which are pouches of fat beneath their jaws that can make them appear as if they have a double chin. Additionally, female rabbits have V-shaped genitalia while males have oblong testicles. In terms of behavior, females tend to be more territorial and dominant, while males are typically more laid back. Female rabbits are also the primary caregivers for their offspring. Furthermore, males and females have different sexual maturity rates, with male rabbits being more likely to exhibit territorial behavior and spray urine. However, female rabbits are generally more cautious and may be easier to litter train. It is also worth noting that male and female wild rabbits have different territory ranges, and females can have multiple pregnancies simultaneously.
Size and Appearance
When it comes to size and appearance, male and female rabbits do not have significant differences. They are generally the same size, with an average weight of 2 to 4 pounds. Their fur can come in a variety of colors and patterns, depending on their breed. Whether you have a male or female rabbit, you can expect them to be cute and fluffy companions.
Dewlaps in Female Rabbits
One notable difference in appearance between male and female rabbits is the presence of dewlaps in females. Dewlaps are pouches of fat that can be found beneath their jaws, giving them the appearance of having a double chin. This feature is more common in larger breeds of rabbits. While some pet owners may find dewlaps endearing, it is important to note that they can become a health concern if they become too large or cause difficulty in eating or grooming.
Genitalia Differences
The genitalia of male and female rabbits also display distinct differences. Female rabbits have V-shaped genitalia, while males have oblong testicles. These differences are an important factor for breeders or veterinarians when determining the sex of a rabbit. However, for pet owners, this distinction may not have a significant impact on their day-to-day interactions with their rabbits.
Behavioral Differences
In terms of behavior, male and female rabbits can exhibit different patterns. Females tend to be more territorial and dominant in nature, often displaying assertive behavior towards other rabbits or even towards their human owners. On the other hand, males are generally more laid back and less likely to engage in territorial disputes. This difference in behavior can influence the dynamics within a group of rabbits or the relationship between a pet rabbit and its owner.
Parental Responsibilities
When it comes to the care of their offspring, female rabbits take on the primary responsibility. They are equipped with maternal instincts and will protect, feed, and groom their offspring from birth until they are weaned. This is a natural behavior among female rabbits, and they excel at providing the care and attention that their offspring require. Male rabbits, on the other hand, do not play a significant role in parental responsibilities.
Sexual Maturity Rates
Male and female rabbits also differ in terms of their sexual maturity rates. Female rabbits reach sexual maturity earlier than males, typically around 4 to 6 months of age. In contrast, male rabbits may take a bit longer to reach sexual maturity, usually between 5 to 7 months of age. It is important to consider these differences in sexual maturity when deciding on the appropriate time to spay or neuter your pet rabbits to prevent unwanted pregnancies.

Territorial Behavior
Territorial behavior can vary between male and female rabbits. Male rabbits are more likely to display territorial behaviors, marking their territory by spraying urine or exhibiting aggressive behavior towards other rabbits or even humans. Female rabbits, although they can also be territorial to some extent, tend to be more cautious and less prone to these behaviors. Proper training and socialization can help minimize territorial issues in both male and female rabbits.
Litter Training
Female rabbits generally tend to be easier to litter train than males. They are more naturally cautious and have a tendency to be cleaner in their habits. This can make the litter training process smoother and faster. However, with patience and consistency, male rabbits can also be successfully litter trained. It is important to provide a suitable litter box and reward them for good litter box habits to encourage positive behavior.

Territory Ranges in Wild Rabbits
In the wild, male and female rabbits have different territory ranges. Female rabbits typically have smaller ranges and tend to be more sedentary, staying closer to their nests and burrows. This is because they are responsible for caring for their young and need to be available to provide for their offspring’s needs. In contrast, male rabbits have larger territory ranges as they may need to cover more ground to find mates and establish dominance within their territories.
Multiple Pregnancies
Unlike humans, female rabbits have the ability to have multiple pregnancies simultaneously. This means that a female rabbit can be pregnant while still nursing a previous litter. This unique reproductive capability allows female rabbits to have a large number of offspring within a relatively short period. However, it is important for rabbit owners to consider the potential challenges and responsibilities associated with multiple pregnancies if breeding their rabbits.
Understanding the differences between male and female rabbits can be essential for both pet owners and those who encounter wild rabbits. Whether it’s recognizing the subtle distinctions in genitalia and appearance or understanding the variations in behavior and territoriality, having this knowledge can help create a harmonious and well-informed environment for these furry friends.