In “The Impact of Rabbit Numbers on Predator Populations,” experts weigh in on the difficult task of determining whether there has been an increase in rabbit numbers compared to previous years. However, one thing that is clear is that the rise in rabbit populations has led to an increase in predators such as foxes and coyotes. Some theorists attribute this rise in predators to the loss of habitat due to development. While the Friends of the Ten Mile River Watershed rejoice in the increase in wildlife, Norfolk Animal Control Officer Hilary Cohen remains cautious and acknowledges the many factors that need to be considered. As residents become more educated about wildlife, their awareness may influence the number of reports made to animal control officers. It is vital for individuals to make their yards less hospitable to deter unwanted wildlife, but this can also limit these creatures’ ability to forage and live. With rabbit populations fluctuating significantly throughout the year, it is clear that their abundance has a profound influence on predator populations.
Factors Affecting Rabbit Numbers
Difficulty in Determining Rabbit Population
Determining the exact population of rabbits can be quite challenging for experts. Norfolk Animal Control Officer Hilary Cohen acknowledges the complexity of this task, stating that there are many factors to consider. Some experts argue that it is difficult to determine if there are more rabbits in a particular year compared to previous years. Factors such as variations in weather, availability of food, and other environmental conditions can influence rabbit populations. Therefore, accurately determining the rabbit population can be a complex and nuanced process.
Rabbit Breeding Patterns
One significant factor that affects rabbit numbers is their breeding patterns. Rabbits are known for their rapid breeding. They have the ability to reproduce multiple litters per year. This high reproductive rate contributes to the increasing numbers of rabbits in certain areas. As they breed at a fast rate, they can quickly reach high population densities if conditions are favorable. Understanding the breeding patterns of rabbits is vital when considering their population dynamics.
Effect of Habitat Loss
Habitat loss is another factor that can significantly impact rabbit numbers. Development and human activities like urbanization and deforestation often result in the loss and fragmentation of rabbit habitats. When rabbits lose their natural habitats, they may struggle to find adequate food and shelter. This loss of suitable habitat can lead to a decline in their population or force them to seek alternative habitats, potentially impacting other ecosystems. The loss of habitat due to development is one theory explaining why predator populations have increased.
Relationship Between Rabbit and Predator Populations
Increase in Predator Numbers
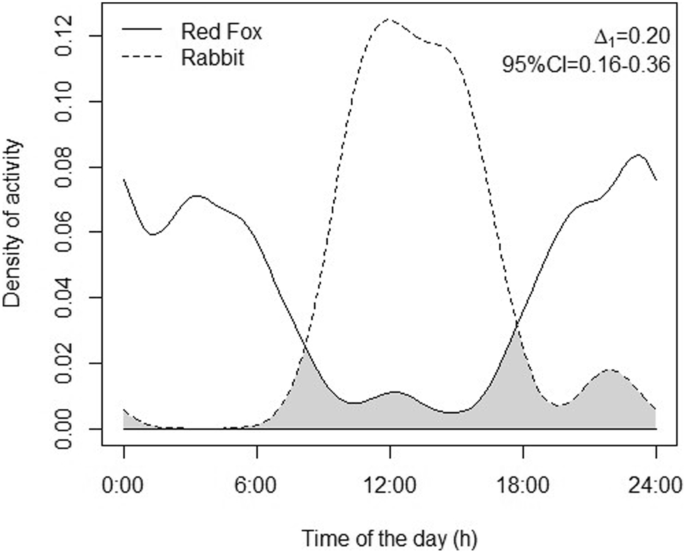
The increase in rabbit numbers has led to a subsequent increase in predator populations. As rabbits become more abundant in certain areas, predators such as foxes and coyotes thrive due to the availability of prey. Foxes and coyotes are opportunistic hunters and will target what is most abundant in terms of prey. Therefore, the rise in rabbit populations directly influences the number of predators in an ecosystem. This relationship between rabbit and predator populations is crucial for understanding the dynamics of wildlife populations.
Impact of Prey Abundance on Predator Diets
The abundance of prey, such as rabbits, can have a significant impact on the diet of predators. When rabbit populations increase, predators may rely more heavily on them for sustenance, leading to a shift in their diet. The increased availability of rabbits can result in a higher proportion of rabbits in the diet of predators like foxes and coyotes. This change in diet can affect the population dynamics of both the predator and prey species, influencing their overall numbers and interactions within the ecosystem.
Effect of Human Education on Reporting
Human education plays a role in the relationship between rabbit and predator populations. As residents become more educated about wildlife and their surroundings, they may be more likely to report sightings of rabbits and predators to animal control officers. This increased reporting promotes awareness of population trends and allows authorities to gather data on rabbit and predator populations. By educating the community and raising awareness about wildlife conservation, humans can contribute to a better understanding of the relationships between rabbits, predators, and their habitats.

Impact on Predator Species
Visible Increase of Fox and Coyote Numbers
In areas with an increase in rabbit populations, it is common to observe a visible rise in the numbers of foxes and coyotes. These predators are highly adaptable and can thrive in diverse habitats. As rabbits become more abundant, foxes and coyotes are attracted to the available food source. Their population expansion is a direct response to the increase in rabbit numbers, indicating the interconnection between these two species.
Predator Adaptation to Rabbit Prey Abundance
Predators such as foxes and coyotes are known for their ability to adapt to changes in prey availability. As the abundance of rabbits fluctuates, predators adjust their hunting strategies to exploit the most readily available food source. This adaptability ensures their survival and can lead to further variations in predator numbers. Understanding predator adaptation is essential in assessing the impact of changes in rabbit populations on the overall ecosystem.
Effect of Habitat Loss on Predators
Habitat loss not only affects rabbits but also has repercussions for predator species. The loss and fragmentation of habitats limit the available territories for predators, which can affect their ability to find suitable food sources. When habitats diminish, predators may face increased competition for resources or may need to travel greater distances to find food. This loss of habitat due to human activities can pose challenges for the survival and stability of predator populations.
Concerns and Implications
Wildlife Increase in the Ten Mile River Watershed
The Friends of the Ten Mile River Watershed are delighted to see an increase in wildlife, including rabbits and predators, within the area. The presence of a diverse and thriving wildlife population is often seen as an indicator of a healthy ecosystem. However, it is essential to monitor these population trends, as both positive and negative implications can arise from such changes. Understanding the concerns and implications of wildlife increase is vital for effective wildlife management and conservation efforts.
Endangered vs. Non-Native Rabbit Species
In Massachusetts, rabbit populations consist of both endangered and non-native species. The New England cottontail is an endangered species, while the eastern cottontail is non-native. The presence of these different species can have varying implications for the ecosystem. The conservation of endangered species is a priority, requiring specific conservation measures and efforts to protect their habitats. The presence of non-native species can have ecological impacts, such as competition with native species. Maintaining a balance between the conservation of endangered species and managing non-native populations is a crucial consideration.
Balancing Wildlife Conservation and Human Needs
The increase in rabbit and predator populations raises the question of how to balance wildlife conservation with human needs. While the presence of wildlife is appreciated, conflicts can arise when wildlife interacts with human activities and developments. It is necessary to find solutions that address both the needs of wildlife and the concerns of humans. Managing habitats, educating communities, and implementing measures to prevent conflicts can help strike a balance between wildlife conservation and human requirements.
Controlling and Managing Rabbit Numbers
Making Yards Less Hospitable
To discourage unwanted wildlife, including rabbits, from inhabiting yards, residents can make their yards less hospitable. This can involve removing potential food and shelter sources, such as overgrown vegetation and uncovered food containers. Additionally, installing physical barriers like fences can help deter rabbits from entering yards. Making yards less attractive to rabbits is a proactive approach to managing their populations and minimizing potential conflicts with humans.
Limiting Rabbit Foraging Opportunities
Limiting rabbit foraging opportunities is another strategy for controlling and managing rabbit numbers. This can involve reducing the availability of food sources for rabbits by keeping yards well-maintained and removing plants that attract them. Additionally, creating an environment that discourages rabbit breeding, such as reducing hiding spots for their nests, can help control their population. By limiting the resources available to rabbits, their populations can be better regulated.
Effects of Rabbit Population Fluctuations
Rabbit populations are known to fluctuate significantly throughout the year. Factors such as seasonal variations in food availability, predation pressure, and reproductive rates can contribute to these fluctuations. Understanding and monitoring these population fluctuations are crucial for effective management strategies. By tracking rabbit population trends, conservationists and experts can implement timely interventions to maintain balanced populations and minimize potential conflicts with humans and other wildlife species.
In conclusion, a complex web of factors affects rabbit populations and their relationships with predators and humans. Determining rabbit population numbers remains challenging due to various influencing factors. The increase in rabbit numbers can lead to an increase in predatory species, such as foxes and coyotes, impacting their population dynamics and diets. Human education plays a role in reporting population trends and understanding the implications of wildlife increase. Balancing wildlife conservation with human needs requires proactive measures and considerations. Controlling and managing rabbit numbers can involve making yards less hospitable, limiting foraging opportunities, and monitoring population fluctuations. By understanding the factors influencing rabbit populations and their relationships with other species, efforts can be made to maintain ecological balance and promote successful coexistence between wildlife and humans.